Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Sparse Binary Sensing Matrices¶
A (random) sparse binary sensing matrix has a very simple design. Assume that the signal space is \(\RR^N\) and the measurement space is \(\RR^M\). Every column of a sparse binary sensing matrix has a 1 in exactly \(d\) positions and 0s elsewhere. The indices at which ones are present are randomly selected for each column.
Following is an example sparse binary matrix with 3 ones in each column
From the perspective of algorithm design, we often require that the sensing matrix have unit norm columns. This can be easily attained for sparse binary matrices by scaling them with \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\).
JAX provides an efficient way of storing sparse matrices in BCOO format. By default we employ this storage format for the (random) sparse binary matrices.
Necessary imports
import math
import cr.nimble as crn
import cr.sparse as crs
import cr.sparse.dict as crdict
import cr.sparse.data as crdata
import cr.sparse.lop as crlop
import cr.sparse.plots as crplots
import numpy as np
import jax
import jax.numpy as jnp
from jax import random
Some random number generation keys
key = random.PRNGKey(3)
keys = random.split(key, 5)
Creating Sparse Binary Sensing Matrices¶
BCOO(uint8[10, 16], nse=64)
If we wish to see its contents
Ad = A.todense()
print(Ad)
[[0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0]
[1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1]
[1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0]
[1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]
[0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1]
[1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0]]
We can quickly check that all columns have d ones
print(jnp.sum(Ad, 0))
[4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4]
By convention, we generate normalized sensing matrices by default. However, in the case of sparse binary matrices, it is more efficient to work with the unnormalized sensing matrix
[[0. 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. ]
[0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0.5 0. ]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0.5]
[0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. ]
[0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5]
[0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. ]
[0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5]
[0. 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0.5]
[0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. ]]
Sparse Binary Sensing Linear Operators¶
It is often advantageous to work with matrices wrapped in our linear operator design. Let us construct the sensing matrix as a linear operator
We can extract the contents by multiplying with an identity matrix
[[0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0]
[1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1]
[1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0]
[1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]
[0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1]
[1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0]]
We can keep the normalization of the sensing matrix has a separate scaling operator
[[0. 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. ]
[0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0.5 0. ]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0.5]
[0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. ]
[0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5]
[0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. ]
[0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5]
[0. 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0.5]
[0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0. 0.5 0. 0. 0.5 0.5 0.5 0. 0.5 0. 0. ]]
Compressive Sensing¶
We shall use a larger problem to demonstrate the sensing capabilities of the sparse binary sensing operator.
Let us construct the unnormalized as well as normalized sensing operators. We shall use the unnormalized one during sensing but the normalized one during reconstruction.
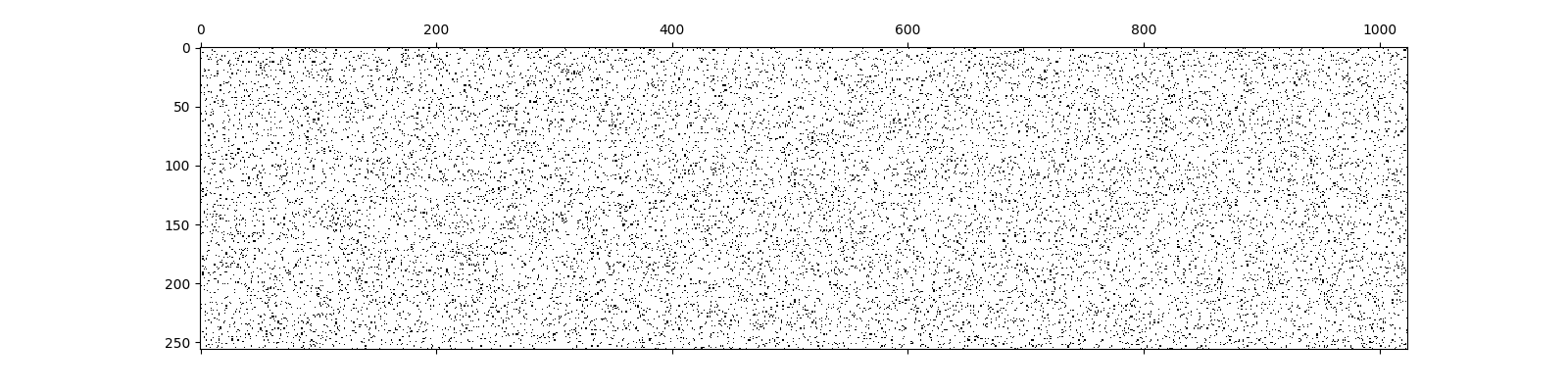
We can quickly visualize the sparsity pattern of this sensing matrix
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f1ffb1d09a0>
Let us construct a sparse signal
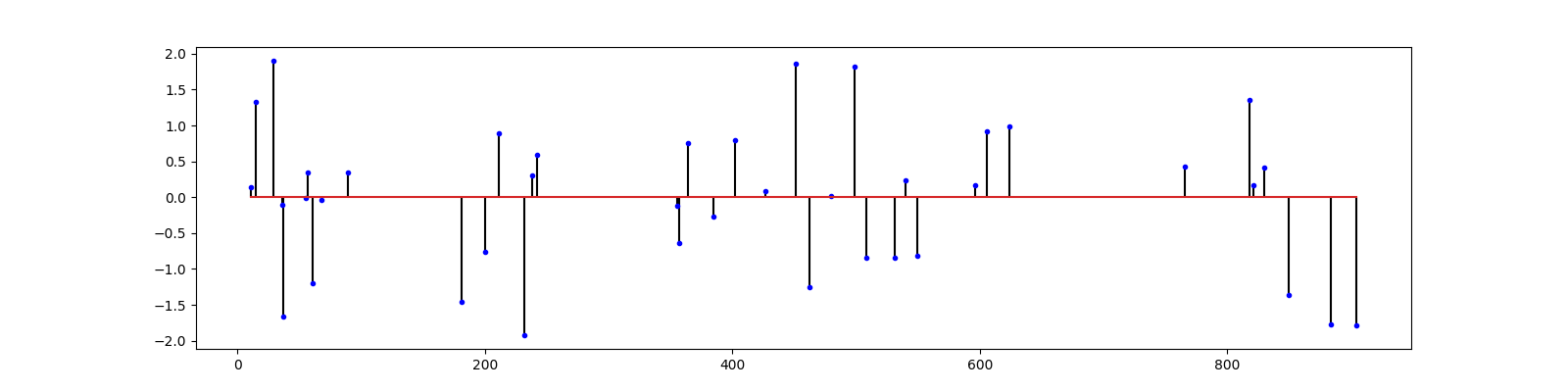
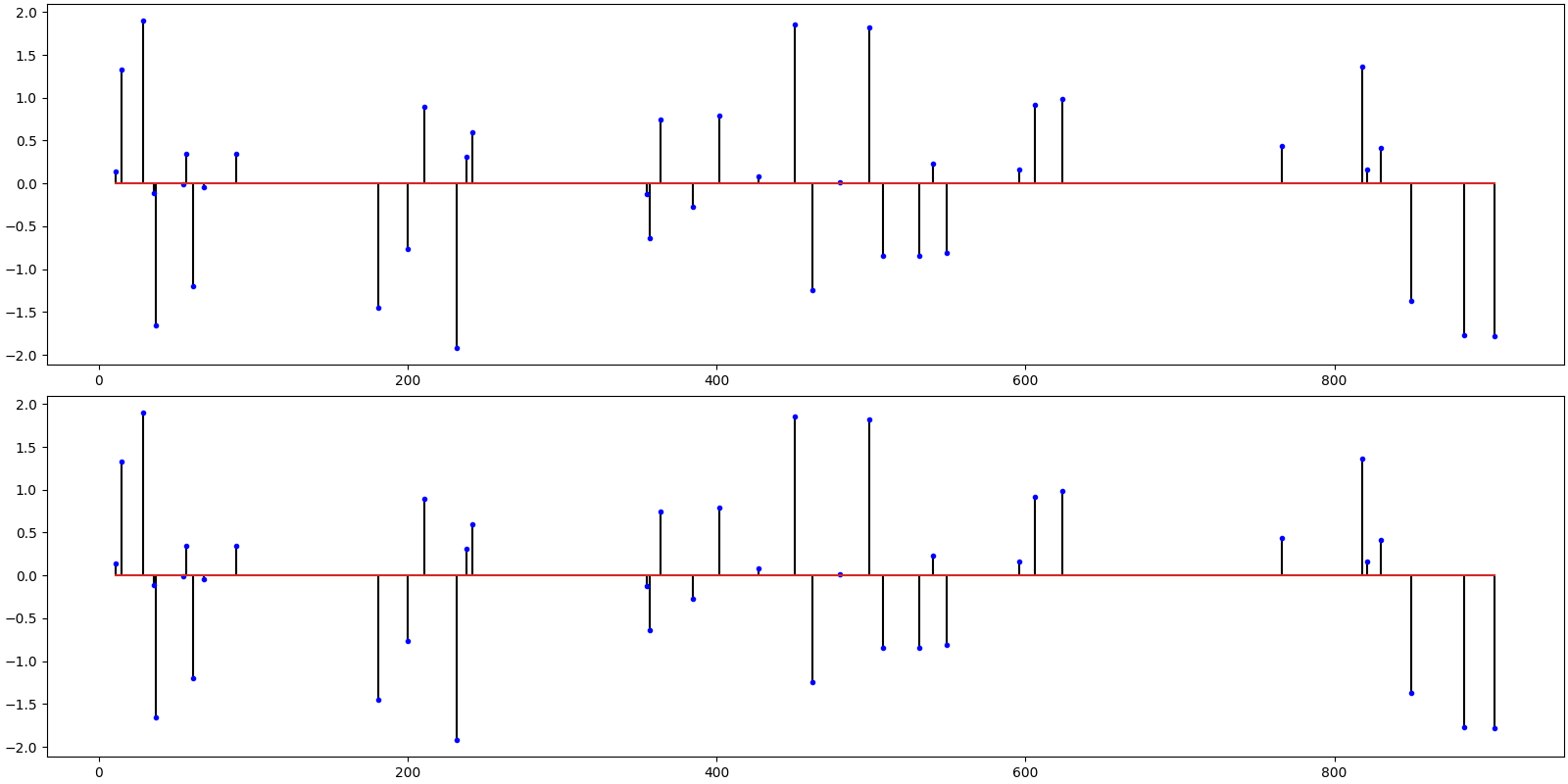
Sparse Recovery¶
We shall use various algorithms for reconstructing the original signal
CoSaMP¶
# Import the algorithm
from cr.sparse.pursuit import cosamp
# Solve the problem
sol = cosamp.operator_solve_jit(T_normed, y, k)
print(sol)
# We need to scale the solution since the measurements were unscaled
x_hat = sol.x * d_scale
# Compute the SNR and PRD
print(f'SNR: {crn.signal_noise_ratio(x, x_hat):.2f} dB, PRD: {crn.percent_rms_diff(x, x_hat):.0f} %')
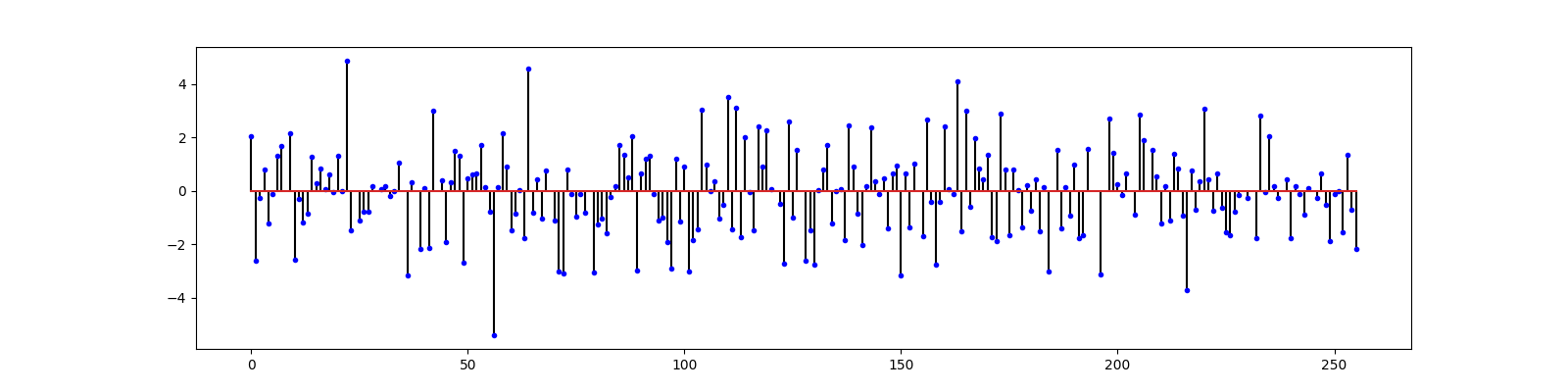
# Plot the original and the reconstructed signal
ax = crplots.h_plots(2)
crplots.plot_sparse_signals(ax, x, x_hat)
iterations 7
m=256, n=1024, k=40
r_norm 4.468207e-14
x_norm 2.590201e+01
SNR: 296.00 dB, PRD: 0 %
Subspace Pursuit¶
Import the algorithm
from cr.sparse.pursuit import sp
# Solve the problem
sol = sp.operator_solve_jit(T_normed, y, k)
print(sol)
# We need to scale the solution since the measurements were unscaled
x_hat = sol.x * d_scale
# Compute the SNR and PRD
print(f'SNR: {crn.signal_noise_ratio(x, x_hat):.2f} dB, PRD: {crn.percent_rms_diff(x, x_hat):.0f} %')
# Plot the original and the reconstructed signal
ax = crplots.h_plots(2)
crplots.plot_sparse_signals(ax, x, x_hat)
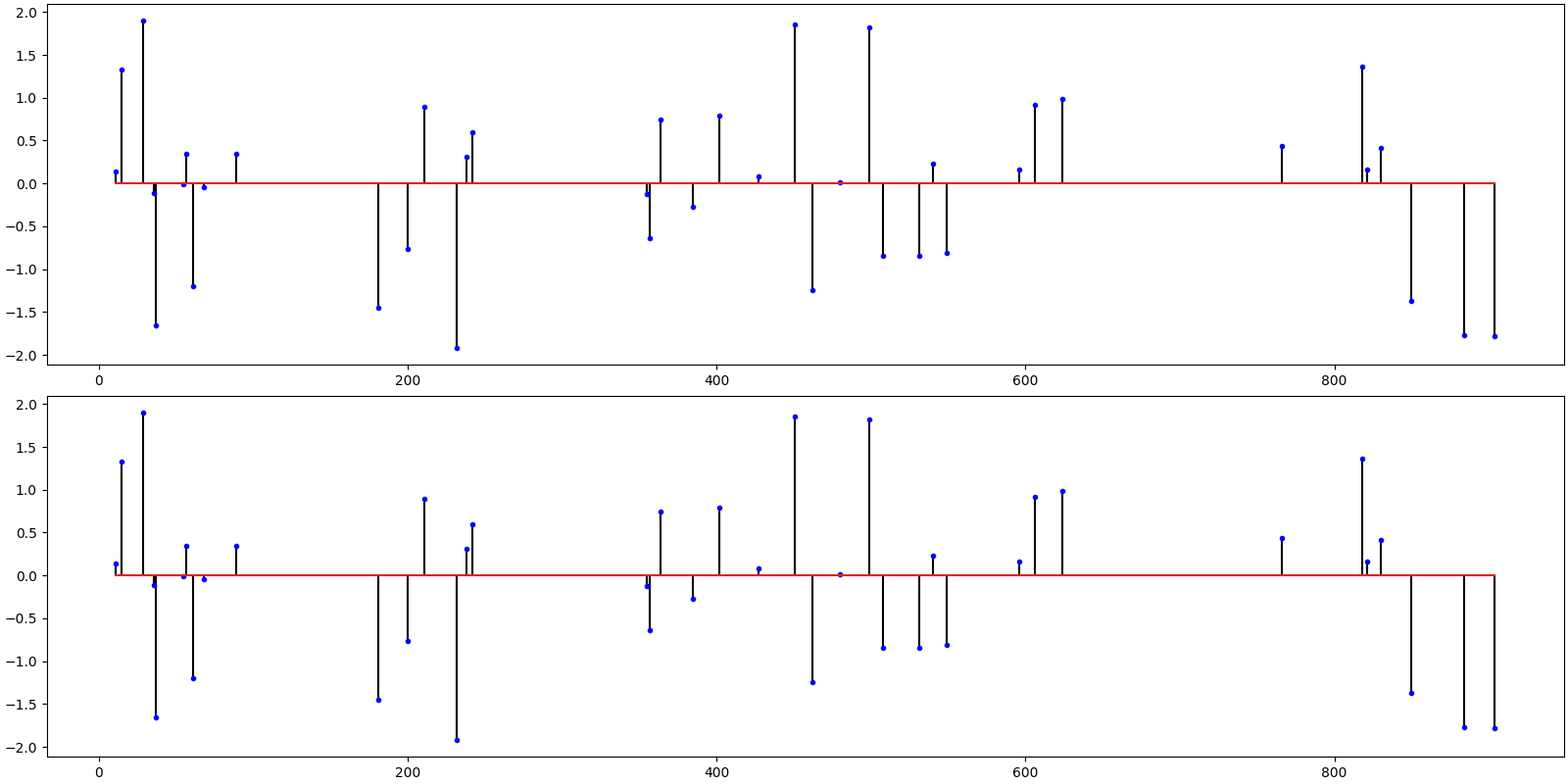
iterations 6
m=256, n=1024, k=40
r_norm 4.307734e-14
x_norm 2.590201e+01
SNR: 295.15 dB, PRD: 0 %
Hard Thresholding Pursuit¶
Import the algorithm
from cr.sparse.pursuit import htp
# Solve the problem
sol = htp.operator_solve_jit(T_normed, y, k)
print(sol)
# We need to scale the solution since the measurements were unscaled
x_hat = sol.x * d_scale
# Compute the SNR and PRD
print(f'SNR: {crn.signal_noise_ratio(x, x_hat):.2f} dB, PRD: {crn.percent_rms_diff(x, x_hat):.0f} %')
# Plot the original and the reconstructed signal
ax = crplots.h_plots(2)
crplots.plot_sparse_signals(ax, x, x_hat)
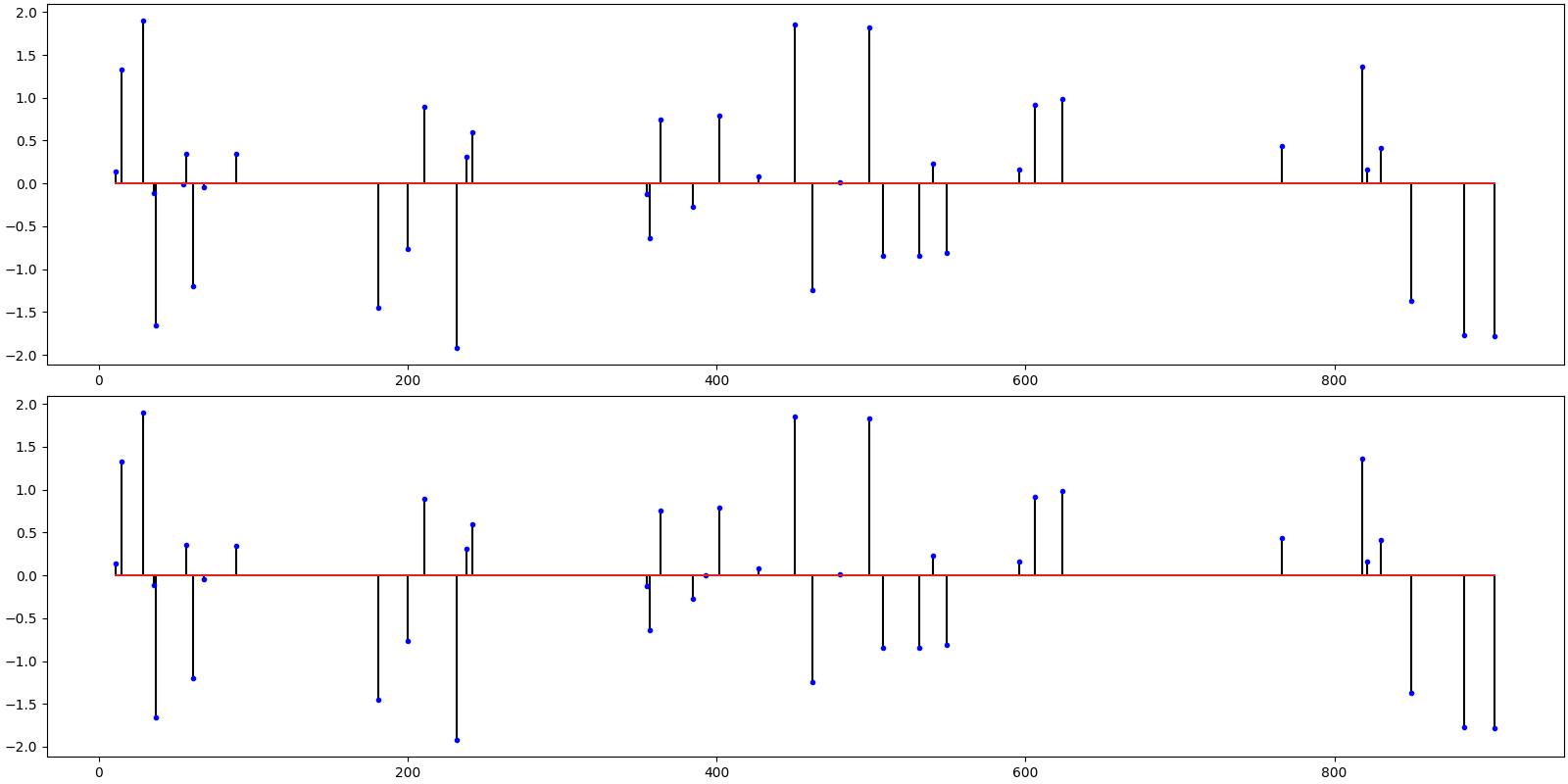
iterations 20
m=256, n=1024, k=40
r_norm 2.904729e-02
x_norm 2.590449e+01
SNR: 56.77 dB, PRD: 0 %
Truncated Newton Interior Points Method¶
Import the algorithm
from cr.sparse.cvx import l1ls
# Solve the problem
# Note that this algorithm doesn't require sparsity level k as input
sol = l1ls.solve_jit(T_normed, y, 1e-2)
print(sol)
# We need to scale the solution since the measurements were unscaled
x_hat = sol.x * d_scale
# Compute the SNR and PRD
print(f'SNR: {crn.signal_noise_ratio(x, x_hat):.2f} dB, PRD: {crn.percent_rms_diff(x, x_hat):.0f} %')
# Plot the original and the reconstructed signal
ax = crplots.h_plots(2)
crplots.plot_sparse_signals(ax, x, x_hat)
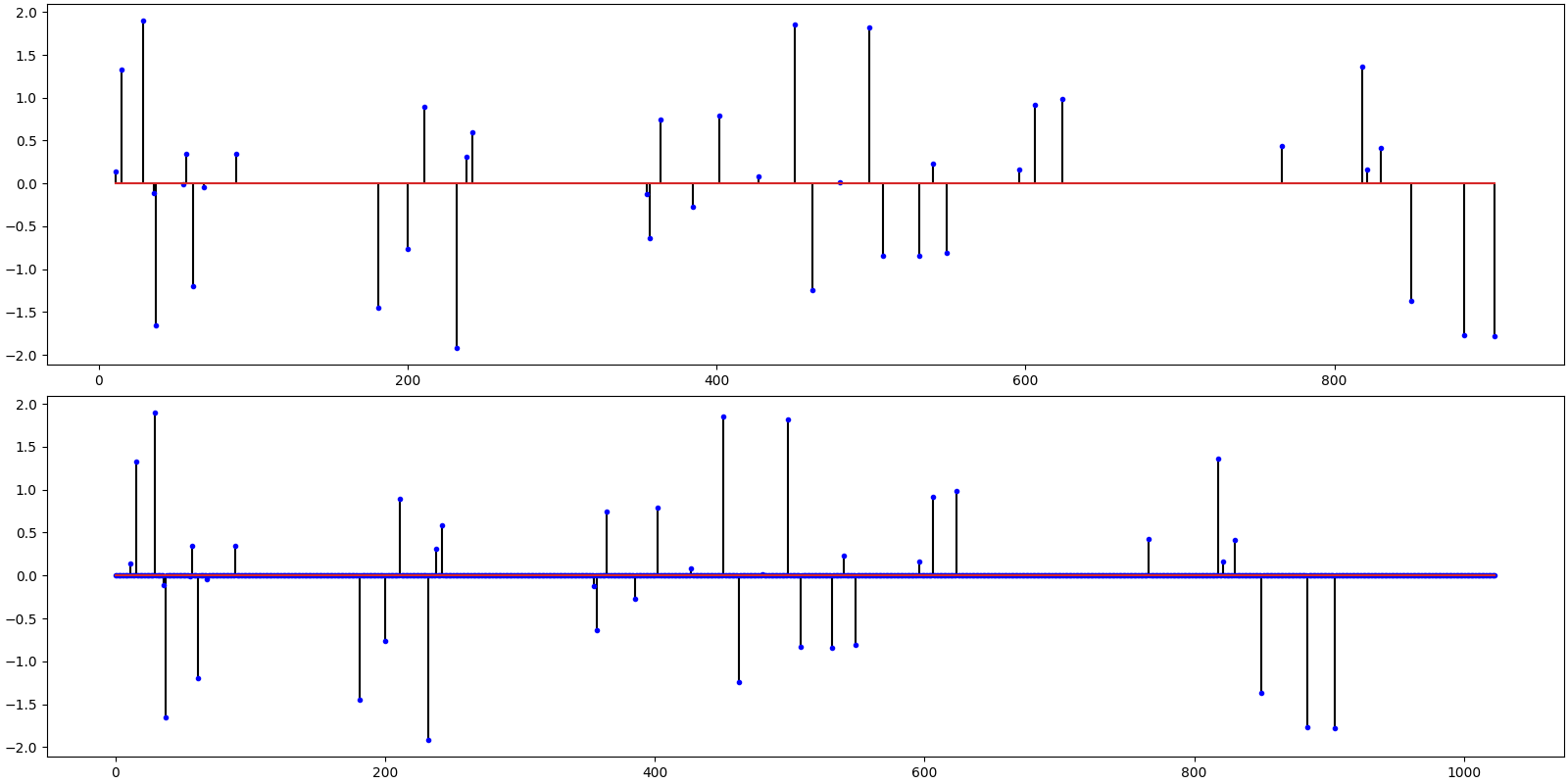
iterations 19
n_times 1121
n_trans 1121
r_norm 3.622522e-02
SNR: 51.38 dB, PRD: 0 %
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 14.304 seconds)
