Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Image Deblurring¶
This example demonstrates following features:
cr.sparse.lop.convolve2DA 2D convolution linear operatorcr.sparse.sls.lsqrLSQR algorithm for solving a least square problem on 2D imagescr.sparse.lop.dwt2DA 2D discrete wavelet basis operatorcr.sparse.sls.fistaFast Iterative Shrinkage and Thresholding Algorithm on 2D images
Image deblurring can be treated as a deconvolution problem if the filter used for blurring the image is known.
Please see the deconvolution example for some background.
Let’s import necessary libraries
import jax.numpy as jnp
# For plotting diagrams
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
## CR-Sparse modules
import cr.nimble as crn
# Linear operators
from cr.sparse import lop
# Image processing utilities
from cr.sparse import vision
# Solvers for sparse linear systems
from cr.sparse import sls
# Several thresholding functions are available in this module
from cr.sparse import geo
# Sample images
import skimage.data
# Configure JAX for 64-bit computing
from jax.config import config
config.update("jax_enable_x64", True)
Problem Setup¶
image = skimage.data.checkerboard()
print(image.shape)
(200, 200)
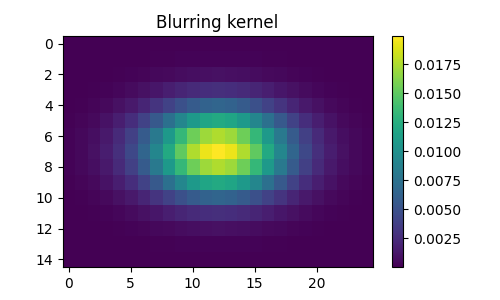
Gaussian blur kernel¶
h = vision.kernel_gaussian((15,25), (8,4))
# plot the kernel
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5, 3))
him = ax.imshow(h)
ax.set_title('Blurring kernel')
fig.colorbar(him, ax=ax)
ax.axis('tight')
(-0.5, 24.5, 14.5, -0.5)
The linear operator for the blur kernel¶
Locate the center of the filter
offset = crn.arr_largest_index(h)
print(offset)
# Construct a 2D convolution operator based on the kernel
H = lop.convolve2D(image.shape, h, offset=offset)
# JIT compile the convolution operator for efficiency
H = lop.jit(H)
(Array(7, dtype=int64), Array(12, dtype=int64))
The blurring¶
Apply the blurring operator to the original image
blurred_image = H.times(image)
# Measure the PSNR
print("Blurred PSNR: ", crn.peak_signal_noise_ratio(image, blurred_image), 'dB')
# plot the original and the blurred images
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].set_title('Original')
ax[1].imshow(blurred_image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].set_title('After blurring')
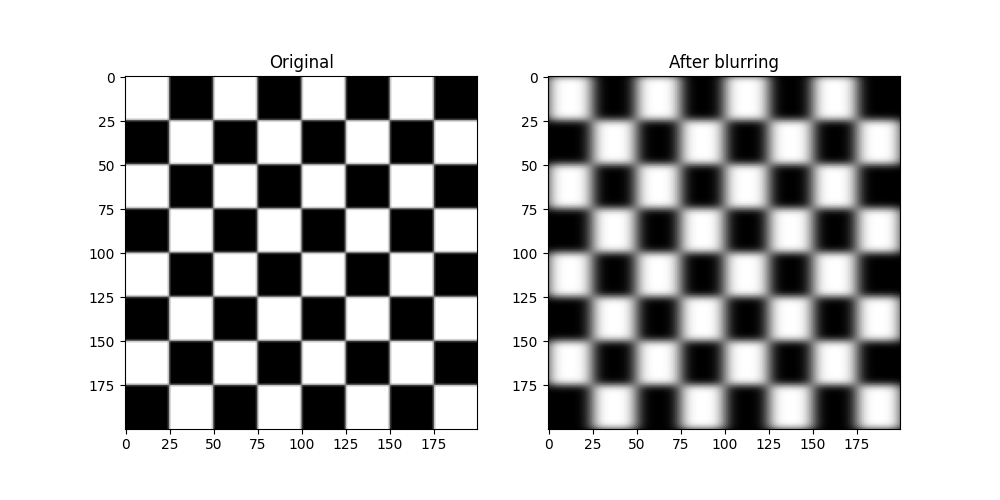
Blurred PSNR: 14.592858290084076 dB
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'After blurring')
The deblurring using LSQR algorithm¶
An initial guess of the deblurred image is all zeros
x0 = jnp.zeros_like(blurred_image)
# We run LSQR algorithm to deblur the image for 50 iterations
sol = sls.lsqr(H, blurred_image, x0, max_iters=50)
deblurred_image = sol.x
# Measure the PSNR
print("Deblurred PSNR: ", crn.peak_signal_noise_ratio(image, deblurred_image), 'dB')
# Plot the original, blurred and deblurred image
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(15, 5))
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].set_title('Original')
ax[1].imshow(blurred_image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].set_title('After blurring')
ax[2].imshow(deblurred_image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[2].set_title('After deblurring')
print(sol)
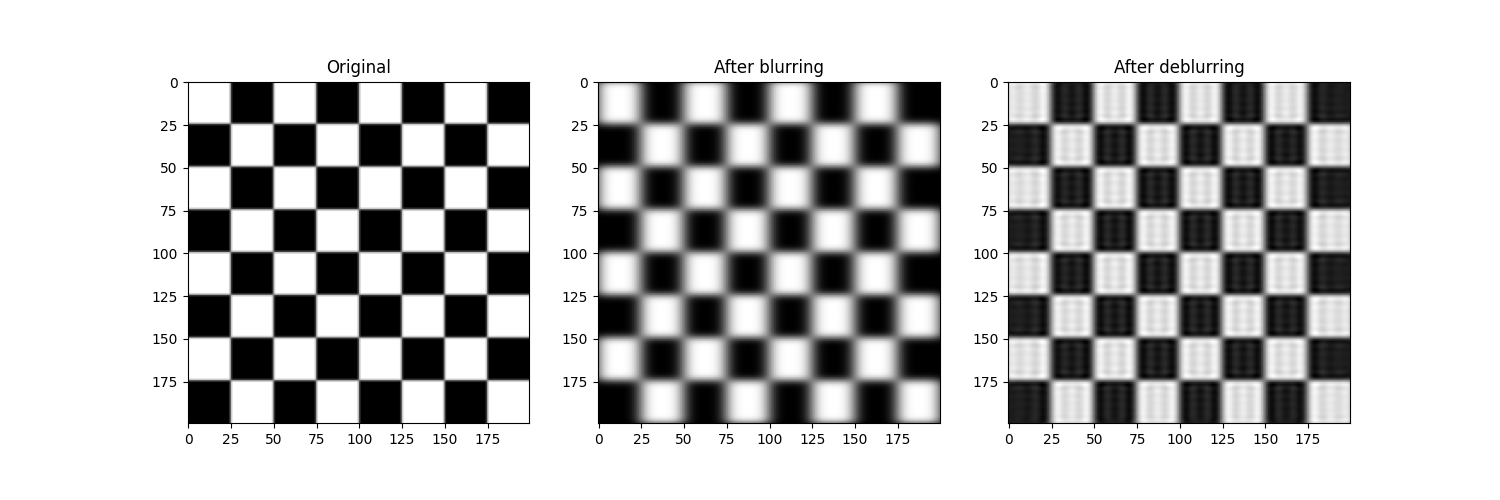
Deblurred PSNR: 21.206455209076868 dB
x: (200, 200)
A_norm: 4.946758875785462
A_cond: 167.30699088560272
x_norm: 34971.66794553033
r_norm: 28.394130441229127
atr_norm: 3.81619135390487
iterations: 50
n_times: 50
n_trans: 50
A wavelet basis for the images¶
Construct the basis
DWT_basis = lop.dwt2D(image.shape, wavelet='haar', level=3, basis=True)
DWT_basis = lop.jit(DWT_basis)
# Visualize the wavelet transform of the image
coefs = DWT_basis.trans(image)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].set_title('Image')
ax[1].imshow(coefs, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].set_title('Wavelet coefficients')
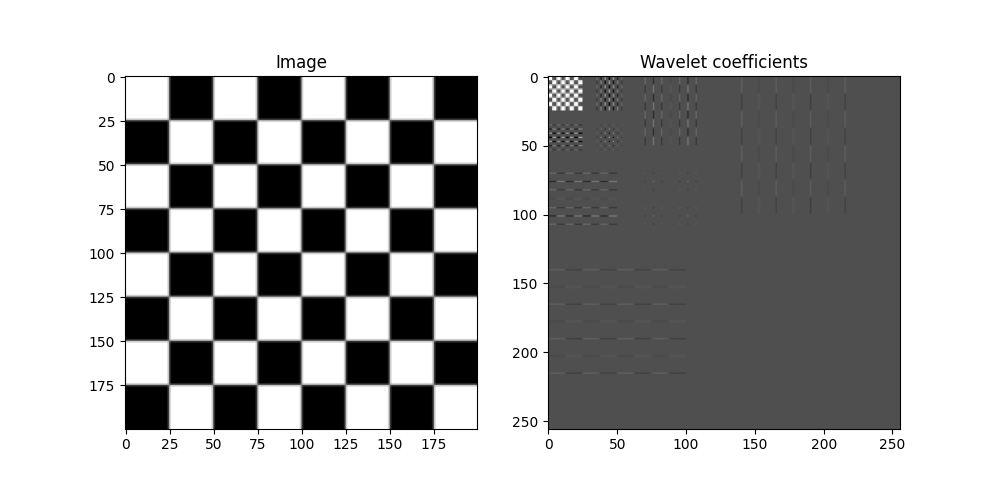
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Wavelet coefficients')
Deblurring with Fast Iterative Shrinkage and Thresholding Algorithm¶
We combine the convolution operator and the wavelet basis operator
A = H @ DWT_basis
# Step size for the FISTA algorithm
step_size = 1.
# Thresholding function for the FISTA algorithm
threshold_func = lambda i, x : geo.soft_threshold(x, 0.02)
# Initial guess for the wavelet coefficients matrix is all zeros
x0 = jnp.zeros(DWT_basis.shape[1])
# Solve the \| A x - b \|_2^2 + \lambda \| x \|_1 problem
sol = sls.fista_jit(
# The combined convolution+wavelet basis operator
A,
# The blurred image as input
b=blurred_image,
# Initial guess for the coefficients
x0=x0,
# Step size for the FISTA algorithm
step_size=1.,
# Thresholding function to be used for FISTA
threshold_func=threshold_func,
# Maximum number of iterations for which the algorithm will be run
max_iters=50)
print(f"Number of FISTA iterations {sol.iterations}")
# Compute the deblurred image from the coefficients given by FISTA
deblurred_image = DWT_basis.times(sol.x)
# Measure the PSNR
print("Deblurred PSNR: ", crn.peak_signal_noise_ratio(image, deblurred_image), 'dB')
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(15, 5))
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].set_title('Original')
ax[1].imshow(blurred_image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].set_title('After blurring')
ax[2].imshow(deblurred_image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[2].set_title('FISTA deblurring')
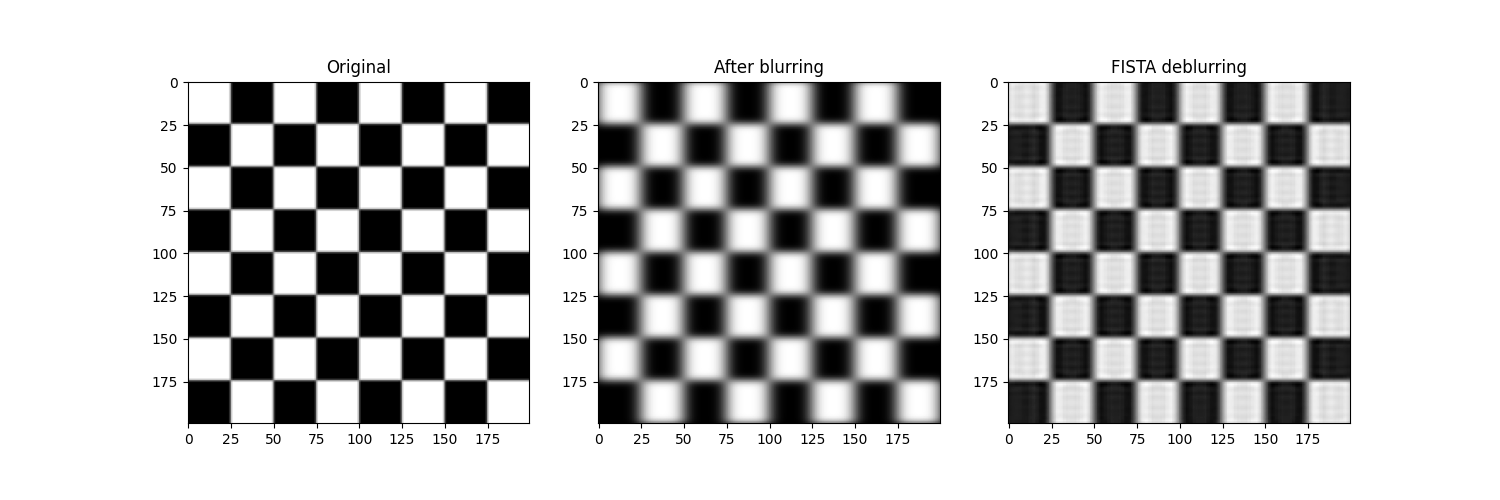
Number of FISTA iterations 50
Deblurred PSNR: 20.411790224661722 dB
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'FISTA deblurring')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 9.313 seconds)
